Any small entanglement of textile fibers that can not be unraveled, formed during carding or ginning. If neps which are on the surface of the fabric, can cause undyed or unprinted spots during dyeing or printing. Neps some time contain immature fibres which are usually weaker than normal fibres.
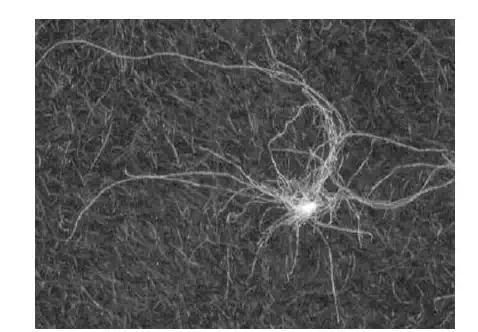
Classification of Neps
For cotton fiber; there are five types of Neps. These are –
· Process Neps: Commonly produced by faulty carding or up to spinning yarn.
· Mixed Neps: Fibres tangle around a foreign materials. For instance – Grit.
· Immature Neps: Generally form by processing immature fibre.
· Homogeneous Dead Neps: A tangle of nearly all dead fibres.
· Fuzz Neps: A fault of short fuzz fibers.
Again we can classified neps according to structure and size into three groups:
· Biological neps
· Seed coat neps
· Mechanical neps
According to size neps are:
· Small neps
· Medium sized neps
· Large neps
Count of Neps
Nep count is the no. of neps per 100 square inches of card web forming (a standerd hank of sliver of 12 NE on a 40 inch wide card).
How To Measure the Count of Neps?
At first a web is collected from the card placed on a 10 inch × 10 inch black board. Then the neps are counted and the no. of neps found is corrected fro any difference in hank or card width.
Mathematically, Nep Count, n = m × 100 [ m = no. of neps per inch square card web





